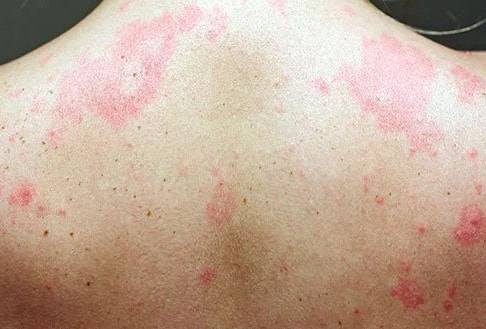
Urticaria is an outbreak of swollen, red bumps or wheals on the skin that appear suddenly and leave no trace when they disappear. It usually causes severe itching anywhere on the body, and swelling (angioedema) of face, lips, tongue, throat or ears may occur. These swellings are harmless, except when occur at the back of the throat which causes breathing difficulty. Acute urticaria last less than six weeks. The most common causes are foods (such as seafood, peanut, brinjal, colouring agents in energy drinks and sweets), medicines, infections, insect bites and internal disease. Chronic urticaria last more than six weeks and 87% of people with chronic urticaria have an unknown cause.
Treatment Options:
Urticaria often goes away on their own or are treated with antihistamines. If it does not respond completely to antihistamines then it may be necessary to use cortisone to control the eruption/itching. In case of breathing difficulty, emergency medicines are administered through intravenous or intramuscular injection.
Urticaria often goes away on their own or are treated with antihistamines. If it does not respond completely to antihistamines then it may be necessary to use cortisone to control the eruption/itching. In case of breathing difficulty, emergency medicines are administered through intravenous or intramuscular injection.